How Does ChatGPT Work?
By Avyya Sharma (CDNP)
89% of students admitted to using ChatGPT for assignments according to a study by Forbes yet most scientists who develop AI can’t fully tell you how it works.
ChatGPT can write essays, generate creative works, assist in scientific research and have in-depth conversations but yet if you were to ask an AI researcher how it does all of this they wouldn’t have a clue. “If we open up ChatGPT or a system like it and look inside, you just see millions of numbers flipping around a few hundred times a second,” said AI scientist Sam Bowman in a podcast with Vox. “And we just have no idea what any of it means.”
ChatGPT doesnt follow a clear set of rules like a traditional computer program but instead learns on its own making connections so that even the creators wouldn’t be able to explain precisely how it works or what they might do.
ChatGPT is a natural language processing (NLP) tool powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. It generates responses to user inputs by leveraging a vast amount of training data. Using this data it is able to do things such as write an article for the guardian:
The AI research company OpenAI developed ChatGPT. The name ‘ChatGPT’ stems from its chat based format as an NLP and the use of Open AI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) technology.
How does ChatGPT work?
In order to fully make the use of something you must fully understand how it works, an idea shared by some of the greatest minds such as Elon Musk.
ChatGPT operates by analysing a text input or a prompt and generating dynamic text in order to respond. It is able to do this because it is a large language model (LLM), essentially a very advanced computer program designed to understand and generate natural language.
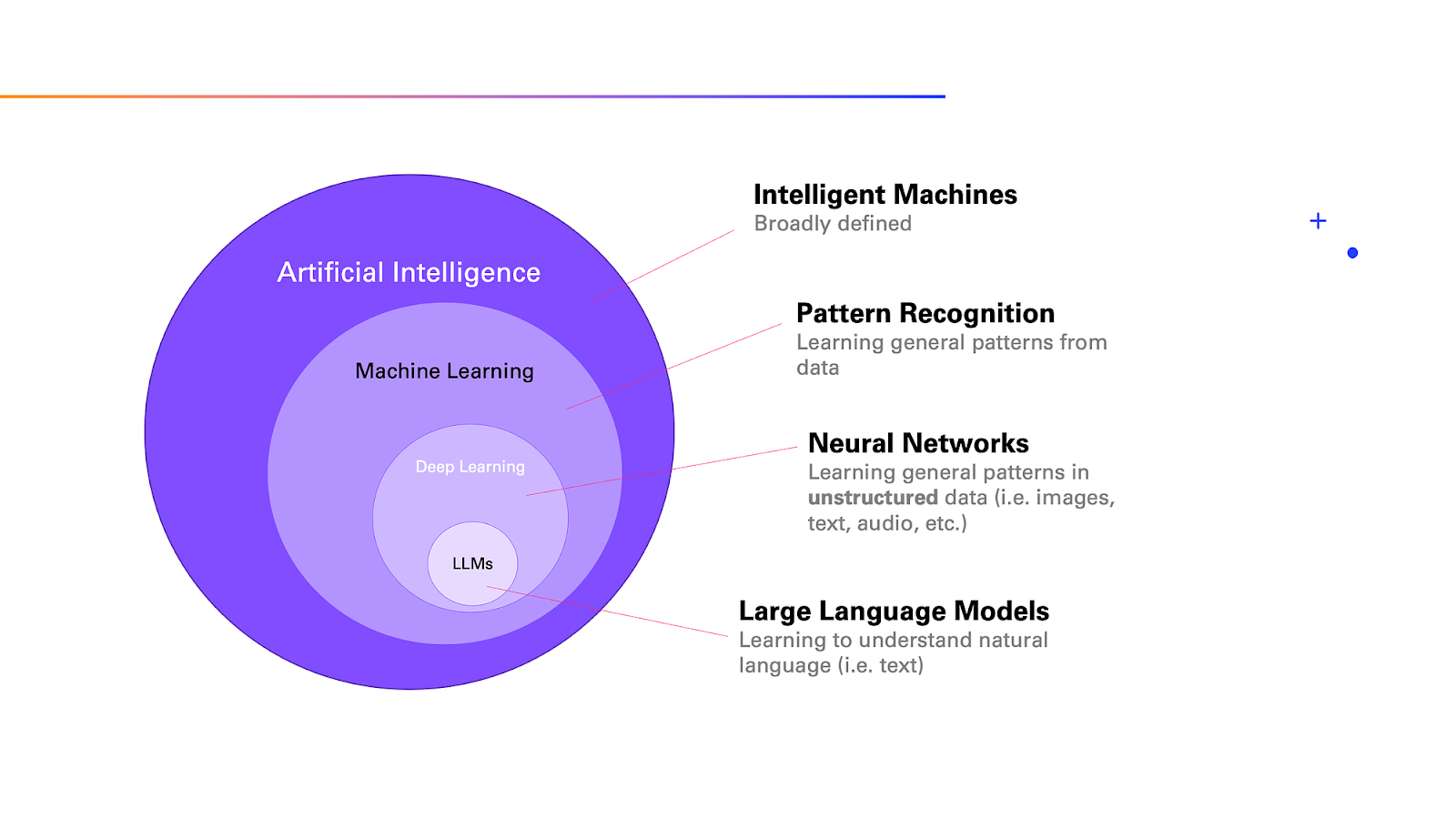
The creators of ChatGPT used a deep learning training process to enable this. Simply, they equipped this system with the ability to process data in a similar way in which the human brain works. Over time, the system learned to recognize patterns in words and follow examples. Eventually it was then able to create its own responses:

According to a research paper by OpenAI, the training data for ChatGPT’s LLM included 45 terabytes (TB) of compressed plaintext. To put that into perspective, one TB is around 6.5 million pages of documents. This training phase was only the start.
How was ChatGPT trained?
Training data:
LLMs like ChatGPT rely on training data, a vast collection of text from millions of sources on many different topics to provide valid and relevant information. The training process begins by compiling this data, which teaches the model language, grammar and context.
For GPT-3 (newest is GPT-4o), the training data came from five main sources:
- Common Crawl: A text collection from billion of web pages, filtered for high-quality material
- WebText2: An extended version of WebText created by OpenAI by looking over Reddit and linked sites
- Books1 and Books2: Two internet-based collections of texts from unspecified published books
- Wikipedia: A complete overview of all the text from every page in the english wikipedia
- Persona-Chat: A data-set owned by OpenAI that contains over 160,000 conversations between participants with a unique persona (which is often used to stimulate conversations with recognizable personalities with traits such as a friendly tone)
Persona-Chat is used to train the conversation aspect of AI, essentially training AI to engage in more varied and natural conversations, tailoring responses to fit different character profiles.
Tokenization
Before being processed by an LLM, training data is tokenized, breaking the text into small chunks called tokens, which can be words, parts of words or characters. For GPT-3 OpenAI used byte pair encoding (BPE) for tokenization. This means the system can create tokens as small as a single character and also represent sentence boundaries. Each token is assigned a unique integer (whole number) at the end of this process, enabling the model to process them more efficiently.
Here is an example of tokens:

Neural Network Development
A neural network is a computer program designed to mimic the structure of the human brain. ChatGPT uses an advanced version of this known as a transformer model. Transformer models can process more text at a time compared to traditional neural networks, allowing them to better understand how each token relates to others. This can help the model grasp the context and the meaning of words quicker and better. For example the phrase “hit the hay” could mean going to bed or physically hitting some hay. Context would help ChatGPT to determine the correct meaning.
Neural networks are essential in any large language model (LLM), powering the algorithms that process and generate text. Open AI’s sophisticated transformer model has revolutionised the field of natural language processing. However first it has to learn the basics in order to carry out these tasks.
Pre-training
To process the information provided by its trainers, the neural network undergoes pre-training. This involves examining each token in the dataset one by one and identifying patterns and relationships to predict missing words in text samples.
During pre-training, the neural network learns to predict the next word in a sequence by analyzing patterns in a vast dataset. For example, the neural network might learn that the word “thank” is followed typically by “you” and the word “want” is often followed by “to”. It stores these patterns as parameters (data points), allowing it to apply learned knowledge to future tasks—similar to how humans use past experiences to understand new concepts. By the end of training, ChatGPT has developed 175 billion parameters, enabling it to generate accurate and relevant responses.
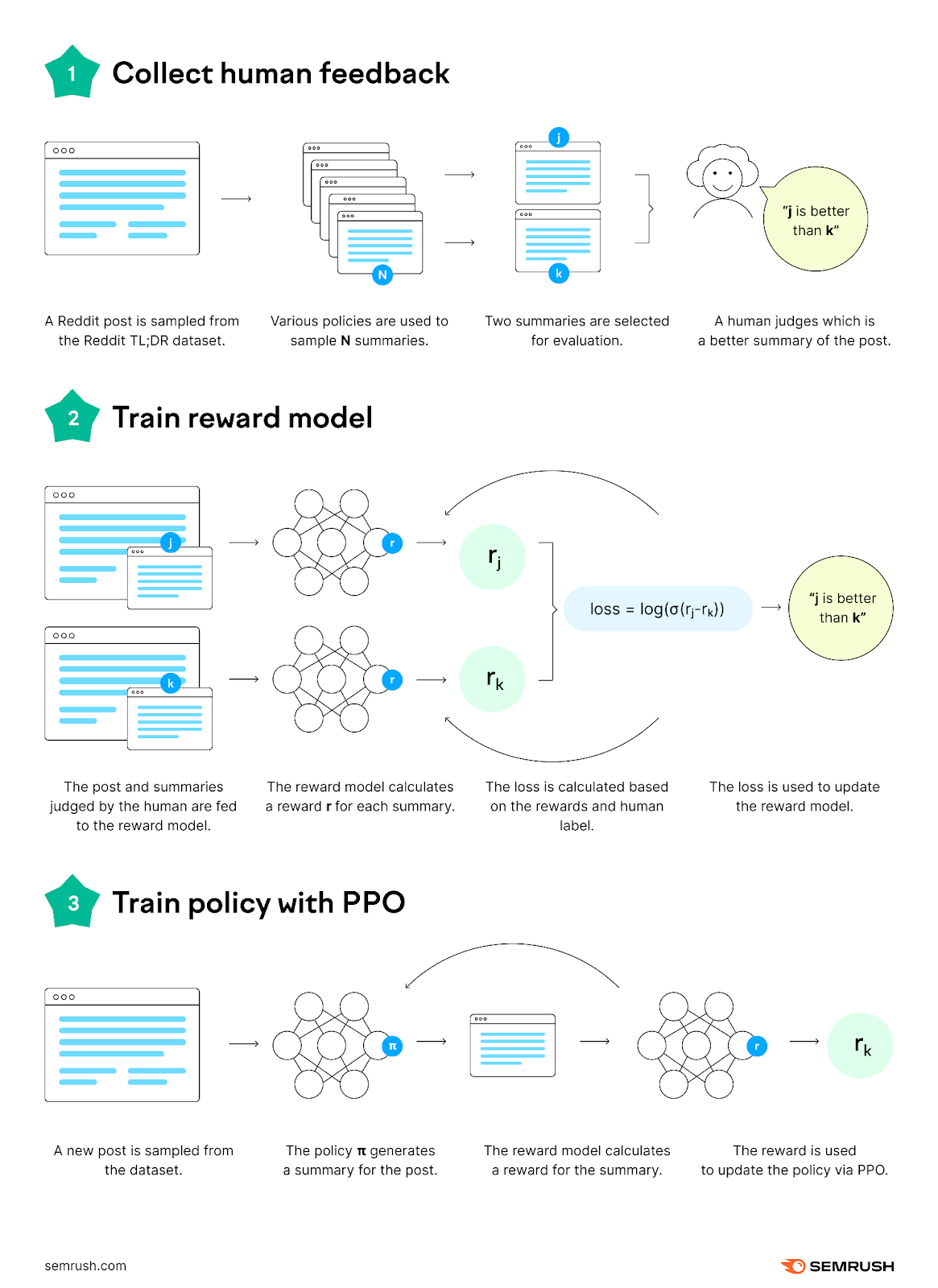
This development process completed by OpenAI also equipped the system with an extensive knowledge base, enabling it to respond with a greater degree of accuracy and variety to many different prompts.
View Bibliography Here